Understanding Sarbanes-Oxley Act Key Compliance Insights
Understanding Sarbanes-Oxley Act: Key Compliance Insights
Navigating Sarbanes-Oxley Act Regulations
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) stands as a landmark piece of legislation aimed at enhancing transparency, accountability, and integrity in corporate governance and financial reporting. Navigating the complexities of SOX regulations requires a deep understanding of its key provisions and implications for businesses, particularly public companies operating in the United States.
Impact on Corporate Governance
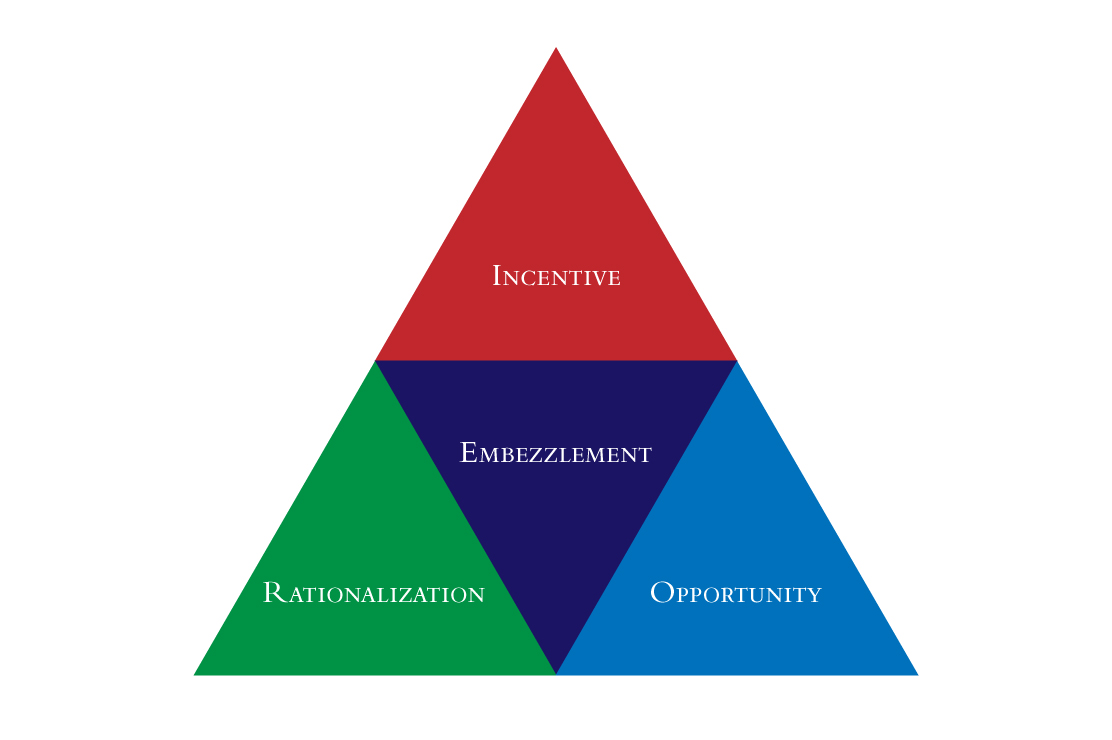
One of the primary objectives of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act is to strengthen corporate governance practices by holding executives and board members accountable for financial reporting accuracy. The Act introduced stringent requirements for financial disclosures, internal controls, and audit procedures, fostering a culture of transparency and ethical behavior within organizations.
Key Features of Sarbanes-Oxley Act
SOX encompasses various key features, including Section 302 (Certification of Financial Statements), Section 404 (Management Assessment of Internal Controls), and Section 802 (Criminal Penalties for Document Destruction). These provisions mandate CEO and CFO certifications of financial statements’ accuracy, internal control assessments, and penalties for fraudulent document alteration or destruction.
Compliance Strategies for SOX Implementation
Implementing SOX compliance requires robust strategies that encompass financial reporting, internal controls, risk assessment, and audit procedures. Companies must establish effective internal control frameworks, conduct regular risk assessments,