Understanding the Impact of Illiquidity on Investments
Understanding Illiquidity in Financial Markets
Introduction
In the intricate world of finance, one term that often sends shivers down the spines of investors and traders alike is “illiquidity.” But what exactly does this term mean, and why is it so crucial in the realm of financial markets? Let’s delve into the depths of illiquidity, exploring its causes, consequences, and strategies for navigating this challenging terrain.
Defining Illiquidity
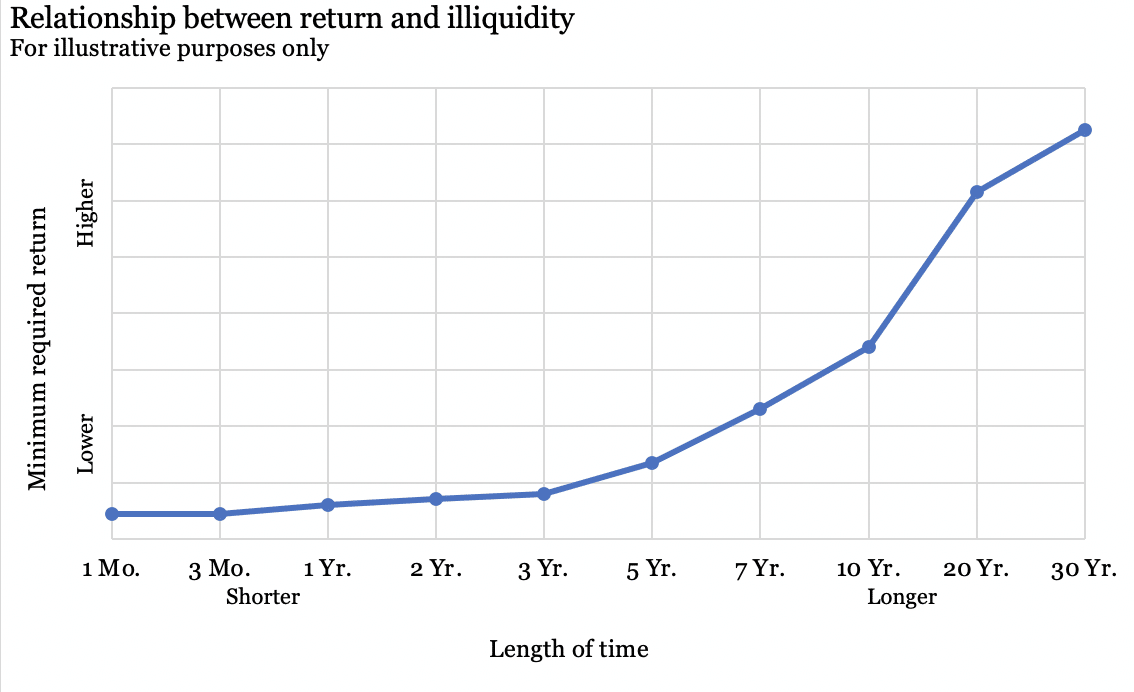
Illiquidity refers to the condition where assets cannot be easily converted into cash without significantly affecting their market value. In simpler terms, it’s akin to trying to sell a rare collectible item in a hurry; finding a buyer willing to pay the desired price quickly can be quite challenging. Similarly, illiquid assets may not find immediate buyers or sellers, leading to price discrepancies and volatility.
Causes of Illiquidity
Several factors contribute to the emergence of illiquidity in financial markets. Market conditions, such as sudden shifts in supply and demand dynamics, can create liquidity crunches. Moreover, asset-specific factors, such as the complexity of financial instruments or restrictions on their transferability, can exacerbate illiquidity issues. Economic downturns and geopolitical events also play a role in drying up liquidity.
Consequences of Illiquidity
The consequences of illiquidity
