Understanding Receivership Key Concepts and Processes
Understanding Receivership: Navigating Financial Turbulence
In the realm of business and finance, the term “receivership” often surfaces during periods of financial distress or legal challenges. It’s a process that can profoundly impact stakeholders, from creditors to company management, and understanding its nuances is crucial for navigating such turbulent waters effectively.
What Is Receivership and How Does It Work?
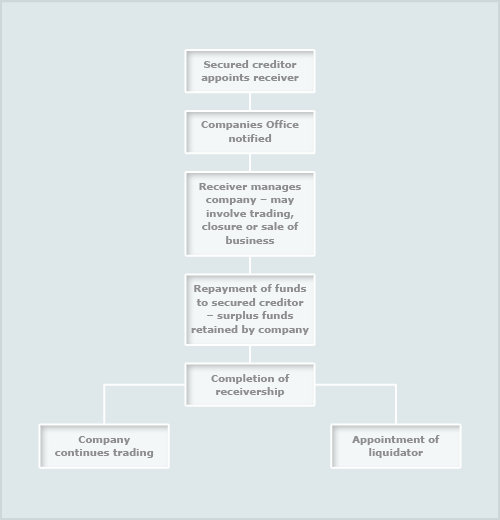
Receivership is a legal status wherein a court appoints a receiver – an independent third party – to take control of a company’s assets and operations. This typically occurs when a business is struggling financially, facing insolvency, or undergoing legal proceedings such as foreclosure or bankruptcy. The receiver’s primary objective is to protect and manage the assets in the best interest of all parties involved.
The Role of Receivers in Financial Management
Receivers play a pivotal role in overseeing the financial affairs of a distressed company. They are tasked with evaluating the company’s financial position, identifying areas of concern, and implementing strategies to mitigate losses. This may involve restructuring debt, selling assets, or reorganizing operations to improve profitability.
Navigating Receivership: Key Considerations for Stakeholders
For stakeholders such as creditors, shareholders, and employees, receivership can evoke uncertainty and anxiety. Creditors may be concerned


